Birth Chart Reading


According to the traditional Hindu system of astrology, the term “Jyotisha” is derived from the Sanskrit word “jyótis”, meaning “light” or “heavenly body.” In India, astrological study is primarily rooted in the principles of Vedic astrology. This sacred knowledge, known as Jyotish Vidya—the science of light—has its origins in the Vedic era and has been practiced since ancient times. It focuses on the celestial and astral patterns that shape human destiny through Vedic Astrology. The philosophy emphasizes that everything in the universe is interconnected, and cosmic influences play a vital role in defining one’s path in life.
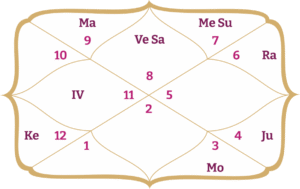
The Role Of Natal Chart In Vedic Astrology:
In Jyotish Vidya, an individual’s birth chart is the most crucial element of astrological analysis. It is considered a roadmap that guides the astrologer through a person’s zodiac, enabling accurate predictions about their future. The natal chart is prepared using the exact time and place of birth, and the analysis is based on the positions of the planets at that precise moment.
According to leading Vedic astrologers in India, these planetary positions reveal a person’s ‘dasha’, the dynamic timeline that maps the course of their life. The combination of houses, planets, and zodiac signs in the natal chart indicates the events likely to occur, while the dasha determines when they will happen.
In Vedic astrology, individuals are understood not merely as their sun signs but as complex personalities shaped by celestial influences. The study of the natal chart begins with the ascendant, the sign rising on the Earth’s horizon at the time of birth. The arrangement of planets and stars in the natal chart provides deep insights into a person’s character, relationships, and life path, reflecting their connection with cosmic energies and shaping their overall personality.
How Does Vedic Astrology Differ From Western Astrology?
Western astrology focuses on the positions of planets and their influence on human life. Developed 2,000–3,000 years ago by the Greeks, this system emphasizes the Sun, the center of the solar system, as having the closest connection with Earth. The Sun’s influence affects the Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn, which in turn impacts all living beings on the planet. This is why Western astrology is also referred to as Tropical Astrology.
According to this tradition, the new astrological year begins around March 22nd, marking the onset of spring and the Vernal Equinox, a day when day and night are of equal length. During the Roman era, January 1st was established as the beginning of the civil New Year; however, this date holds no astrological significance. In Western astrology, Aries, considered the first sign of the zodiac, aligns with the time of the Vernal Equinox, followed sequentially by the other zodiac signs.
EXCELLENTTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Accurate prediction by sir highly recommended....Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Best astrologerPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Experience is superb. Great KnowledgePosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Best Astrologer..good to consult..very helpful😊Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Thank you so much sir for having a pep talk with me pretty openly. Your words were healing and assuring too, providing deep insights with clarity. I felt very positive about the reading and really appreciate you for comforting me and my soul. Thankyou 🙏🏻Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Best and most helpfulPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Best place for Astrology consultancyPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. "Life-changing experience! The Financial Astrology class gave me deep insights into how planetary movements truly impact markets, wealth, and decision-making. The concepts were explained in a very simple yet powerful way, blending astrology with practical financial wisdom.Verified by TrustindexTrustindex verified badge is the Universal Symbol of Trust. Only the greatest companies can get the verified badge who has a review score above 4.5, based on customer reviews over the past 12 months. Read more

Top 7 Reasons of Divorce in Astrology (As Per Vedic Astrology Chart)
Divorce is not a sudden event. It is the final outcome of emotional, mental, and karmic pressures that slowly build


Daily Horoscope – December 7, 2025 | A Calm Start, Clear Thoughts & Soft Emotional Shifts
Welcome to your horoscope for December 7, 2025. The day starts slow, steady, and peaceful thanks to the Moon in


Daily Horoscope 5 December 2025 | A Moody Morning, A Calmer Evening & A Day Full of Heartfelt Shifts
Welcome to your daily horoscope for 5 December 2025. If your morning felt a little restless or emotionally confusing, you’re


Daily Horoscope – 4 December 2025
Astrology isn’t about making life dramatic — it’s about understanding the energy of the day so you can move with


The Last Supermoon of 2025 Will Rise This Week: A Complete Guide
The night sky is preparing for one of the most anticipated events of the year. The last supermoon of 2025
What Astrology Sign Is January? (Capricorn or Aquarius Explained)
January is a unique month in astrology because it carries two zodiac signs: Capricorn and Aquarius. With the new year

